Evolution Towards 6G

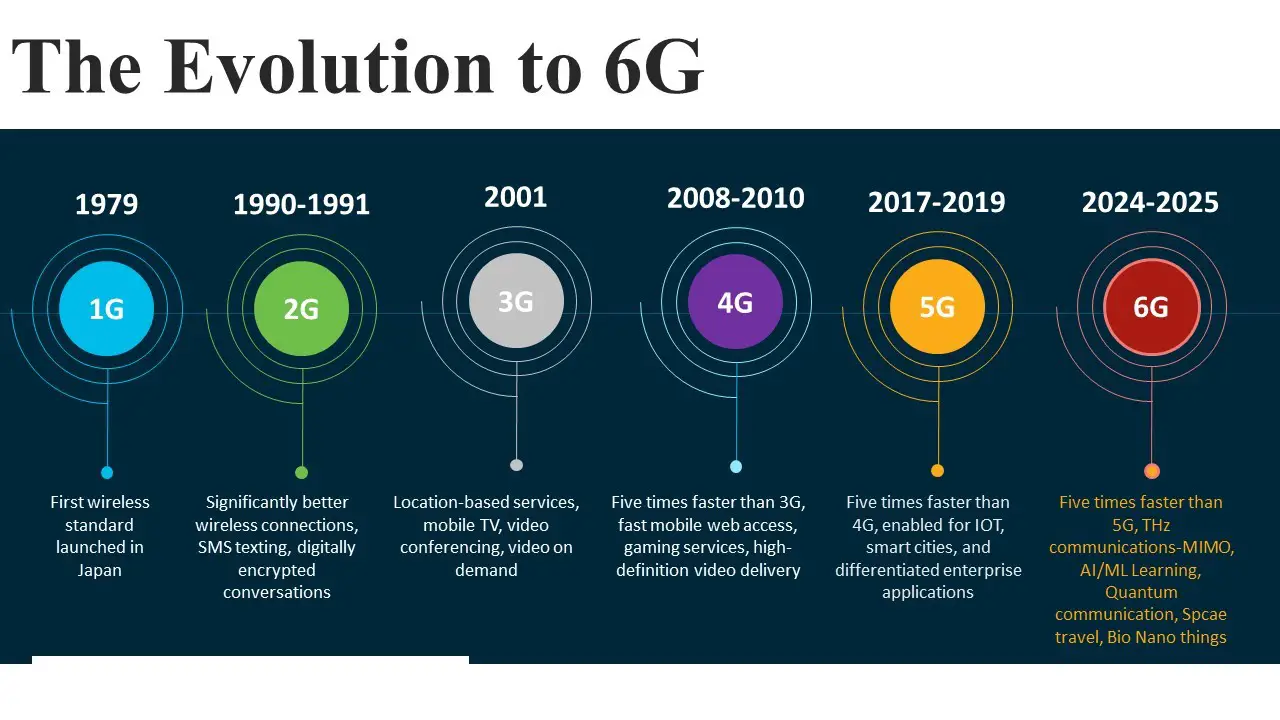
Today as we speak, a total of 195 operators in over 60 countries and regions had launched mobile 5G services (and the number gets even bigger when we add 3GPP compliant 5G services such as fixed wireless). While 5G network deployment will continue in various parts of the world, including countries like India where 5G services are yet to be launched (or say, soon to be launched), the focus of wireless research is moving towards 6G. In keeping with the tradition of rolling out a new generation of cellular tech once every ten years, it is expected that 6G tech will be standardized with deployment starting around 2030.
Why Do We Need 6G?
6G will fuse the human, physical and digital worlds. It will deliver a network that takes us from connectivity to togetherness, from information to knowledge and from purpose to effectiveness. 6G will help us redefine how we live, work and take care of our planet.
How will it change our lives and society?
Let’s start with the devices that humans can use to connect to the network. While smartphones and tablets will still be around, we are likely to see new man-machine interfaces that will make it much more convenient for us to consume and control information. For example: ● Touchscreen typing will become obsolete. Pointing and talking to the devices we use to get things done will become the norm. ● The devices we use will be fully context-aware, and the network will become increasingly sophisticated at predicting our needs. ● Wearable devices, such as earbuds and devices embedded in our clothes, skin patches and bio implants will become commonplace. That’s not all. Holographic telepresence will become the norm for work and social interaction, while dynamic digital twins will be an essential platform for augmenting human intelligence with increasingly accurate, synchronous updates of the physical world. Industrial use cases with extreme communication requirements will also rely on 6G. Furthermore, we can expect latency to fall to microseconds and network reliability to increase through simultaneous transmission over multiple paths involving multiple hops. We will be looking at Tbps of speed and connecting “trillions” of objects.
How is 6G different from previous technologies?
In every generation up to 5G, spectrum, spectral efficiency and spatial reuse were the three fundamental dimensions for system design. In the case of 6G, three new fundamentals will also come into play alongside the above three: Data: Network and sensor data will become the fundamental resource to exploit to improve 6G system performance. Compute: Leveraging computing that is available in the local area, but isolated from devices, will be a new theme in the 6G timeframe. Energy: Energy consumption of both the network and the devices will be highly scrutinised. The energy available at each element of the network will determine the achievable performance.
Networks with a sixth sense
The 6G generation will likely leverage the network primarily through the application of sixth sense capabilities. Thus it will be all about application in the 6G generation, as human-to-person interaction will now see humans connecting to the digital world, rather than just human-to-machine. This will mean that a foolproof, private network may not only be suitable for stopping a car, but by itself a kind of sixth sense and intuitive understanding of intentions can be created in the 6G network, making interactions between humans and the physical world more productive through anticipation.
Where do we stand vis-à-vis 6G?
Globally, there are already several projects in the 6G space, including the North American Next G Alliance (with Nokia as a founding member), the European Union launched flagship Hexa-X research project (Nokia is the overall lead). The Nokia Standards team in India, part of the Strategy and Technology (S&T) division, is making significant contributions to Nokia’s global initiatives for 6G development and standardization. On the domestic front, there are three major platforms that are driving the 6G pre-standardisation initiative in India – 6G Technology Innovation Group under DOT, TSDSI (Telecommunications Standards Development Society, India) and 6G India Forum under COAI. The Nokia Standards team is actively supporting these initiatives, with the aim to make a significant contribution to global 6G technology development by enhancing India’s competencies.
Paving the way for 6G
Nokia Bell Labs expects 6G wireless technology to launch commercially by 2030. Standardisation Phase 1 is likely to begin by 2025, leading to the first 6G specification in 3GPP Release 21 by 2028. This will be followed by commercial deployment around 2030. 5G-Advanced, the next standard enhancement to 5G, will act as a bridge between 5G and 6G. 6G will transform our lives and societies for the sustainable development of mankind will build on the capabilities of 5G and 5G-enhanced to transform the digital world. All stakeholders need to come together to ensure that we maintain the momentum for 5G, especially for countries like India, while we lay the foundation for 6G.
Read Also:
- Towards 6G: Future Communication Technology
- General Architecture Of Wireless Technology
- 6G Technology
- Cell-Phone Technology
- 6G and 7G Cellular Network Technology
Recent Posts
US President’s Big Claim, India Agrees To Reduce Tariff: US Will Impose ‘Tit For Tat Tax’ From Tomorrow; China, Japan, South Korea United Against It
US President Donald Trump is going to impose tit for tat tax across the world…
America Will Impose ‘Tit For Tat Tariff’ From Today: Trump Will Announce It At The Make America Wealthy Again Event; Israel Removes Custom Duty On American Products
US President Donald Trump will announce the imposition of tit for tat tariff (reciprocal tariff)…
America Imposed 26% ‘Tit For Tat Tariff’ On India: Trump Said- Modi Is A Good Friend, But Is Not Behaving Properly; New Tariffs Will Be Implemented From April 9
US President Donald Trump on Thursday announced to impose 26% tit for tat tariff (reciprocal…
Decline In The Price Of Gold And Silver: Gold Fell By ₹ 119 To ₹ 90,996, Silver Is Being Sold At ₹ 99,536 Per Kg; See The Price Of Gold According To Carat
The price of gold and silver fell today i.e. on 2 April. According to the…
Value Of 8 Of The Top 10 Companies Increased By ₹88 Thousand Crores: HDFC Bank Is The Top Gainer, Market Cap Increased By ₹44,934 Crores, Infosys’ Value Decreased By ₹9000
In terms of market valuation, the market value of 8 of the 10 largest companies…
Musk Sold X To His Own Company Xai: Deal Done For ₹2.82 Lakh Crore, Bought In 2022 For ₹3.76 Lakh Crore
Elon Musk has sold his social media company X to his own artificial intelligence (AI)…


