In most developing countries, which are most affected by pollution, the effects of pollution are still poorly reported. This is due, in part, to poor and unreliable database management systems and, in part, to lack of awareness about the harmful effects of pollution on the environment and health. For example, in some parts of Africa, certain health problems, such as birth defects, miscarriage, cancer, developmental deficiencies, and sudden death, are considered to be caused simply by bad luck or “death”, leading to less attention being paid to pollution and its effects. goes. It is well known that social determinants of health, such as income and education levels, are closely linked to public preferences for environmental protection. Thus, in low-income countries, people are more concerned about food and shelter than health and environmental protection, leading to increased pollution and its effects in these countries.
1. Environmental Impact
When pollution increases, it is called pollution because in most cases the environment is the most affected. Land, water, air and biosphere constitute the environment and all act as reservoirs of pollutants. Impacts on land include contamination of the land surface by waste (causing foul smell and poor aesthetics), damage to trees, death of wildlife species, soil infertility resulting in reduced crop yields, destruction of roof panels. Historical monuments and buildings are affected, and cars and vehicles become discolored. In particular, the continuous mining process destroys the vegetation/soil system, thereby reducing soil productivity and fertility (Feng et al., 2019). On the other hand, other human activities damage landscapes, such as: habitat destruction, soil erosion, extinction of animals, loss of resources such as wetlands and coastal ecosystems (Valero and Valero, 2019). The chemical properties of the soil change, leading to the loss of important cationic nutrients such as magnesium, potassium and calcium, and a decrease in soil pH. All this directly or indirectly causes food shortage for humans and other animals. It can even lead to starvation and death.
Furthermore, direct contact between land and water promotes the transfer of pollutants. The effects of pollution on water bodies usually result in changes in their chemical, microbiological and physical properties. For example, an increase in water temperature is a result of increased solar heat. Oil covers the surface of the water in productive areas, blocking oxygen and sunlight. The salinity of water increases due to NaCl used in drilling. The amount of poisonous metals increases. And eutrophication occurs. These changes cause excess nutrients and reduced plant growth, oxygen depletion in water, reduced biodiversity, destruction of biological networks, and degradation of water quality and quantity. As a result of pollution, water bodies become smelly, unpleasant, ugly and desolate due to the entry of sulfur and nitrogen containing compounds and other anaerobic activities. The atmosphere is known to carry various pollutants and deposit them in water and land. When sunlight collides with certain pollutants such as particulate matter and gases, it creates haze and affects the color and clarity of the shape of objects. M.P. on soil and aquatic environment. The effects are being investigated. However, M.P. May contain hazardous additives and chemicals that can enter the soil ecosystem and accumulate in soil invertebrates. Such accumulation in earthworms can affect the earthworms’ immune system response, biomass, growth, and even reproduction. All these effects of environmental pollution are directly or indirectly related to human and animal health.
2. Effects On Human Health
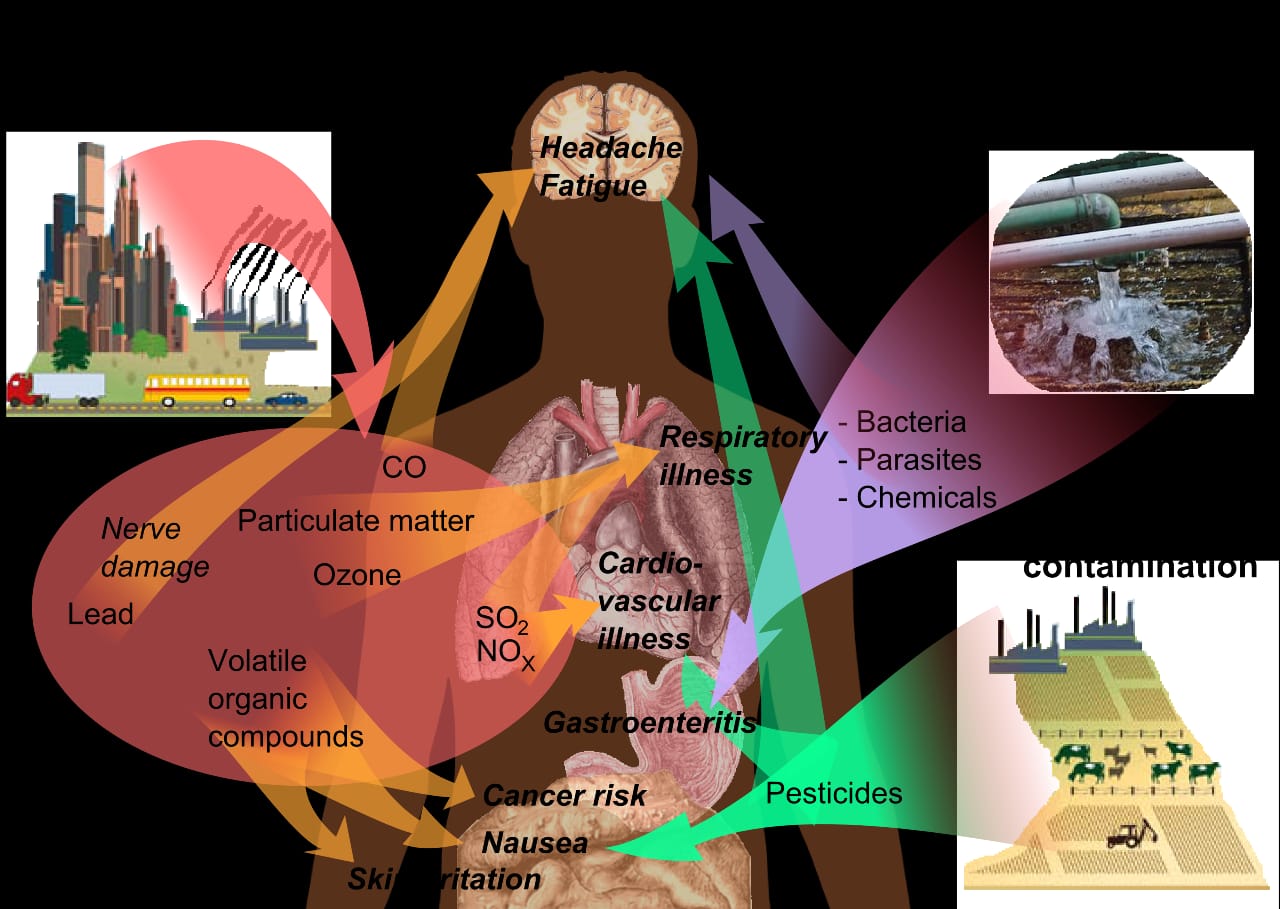
Is it “karma” that the products of human activities come back to haunt him? The impact of pollution on health is so great that most of the diseases caused to humans are caused by pollution. Recent studies have increasingly uncovered evidence showing a link between pollution and a number of serious health conditions. Among these studies, studies focusing on the health effects of air pollution have increased at an alarming rate. A World Health Organization report clearly shows that indoor air pollution caused by cooking and burning is responsible for 3.8 million deaths (WHO, 2018). As expected, this figure ranged from 10% in low- and middle-income countries to 0.2% in high-income countries.
Additionally, the Global Burden of Disease reported that particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of less than 2.5 mm (PM 2.5), a component of ambient (or outdoor air) pollution, is the fifth largest risk factor for death worldwide, which Affected 4.2 million people in 2015 and resulted in more than 103 million disability-adjusted life years lost (Schrafnagel et al., 2018). Shortening of telomere length in newborns is believed to be associated with exposure to PM2.5, PM10, CO, and SO2 during the third trimester of pregnancy (Song et al., 2019). This means that these pollutants are not only dangerous for us, but also pose a serious threat to the sensitivity of the fetus. Some persistent pollutants, such as POPs and PAHs, have been found to be tied to PM, especially PM 2.5, and humans. Causing a variety of cardiopulmonary diseases, respiratory diseases, cancer and non-cancer effects.
Airborne pollutants travel longer distances and cause greater harm when they reach a target population, either through inhalation, accumulation in drinking water, or through exposed food, thereby contaminating the target population . Although many other health problems can be traced to pollution, epidemiological studies have shown that many health problems in women can be caused by pollution, especially air pollution. Literature suggests that exposure to PM2.5 and O3 may induce certain genetic or epigenetic abnormalities, which may lead to the development of uterine fibroids (Lin et al., 2019).
3. Impact On Animal Health
Oil spills during exploration, refining and transportation on land, through pipelines and ships have deadly effects on the health of wildlife and marine life. The digestive, respiratory and circulatory systems of these organisms are adversely affected when they inhale or swallow petroleum products containing toxic substances. Seabirds and other marine mammals face risk of mortality due to contamination of their skin and feathers from oil spills, resulting in limited mobility, inability to obtain adequate food, and inability to escape predators. Sea birds are greatly affected by oil spills, but these effects are often not reported. Studies have shown that oil pollution causes the death of birds. Although some oiled birds are detected and reported at the time of their death, many unreported deaths occur due to oil spills (Walker et al., 2019).
The challenges that plastics pose to the environment have been a hot topic recently. They can damage ecosystems, limit biodiversity, and ultimately affect the lives of mainly birds, fish, crabs, turtles, and other marine animals (Barboza et al., 2019). Plastic harms animals directly or indirectly. Direct hazards include internal damage, stress problems due to swallowing which can cause wounds and tears, suffocation and entanglement of aquatic organisms, impaired growth and photosynthesis of primary producers of the food chain such as algae, impaired growth in crustaceans and reproduction (Barnes, 2019). In addition to immediate death, injuries and restricted movement may occur, leading to starvation and escape from predators.
Furthermore, pollution affects the genetic and biodiversity of natural populations. Studies have shown that the genomes of fish living in polluted environments contain highly complex ribosomal sequences. A systematic increase in ribosomal DNA copy number is observed in response to changes in environmental conditions. This is because these sequences are primarily involved in maintaining genome integrity (Araujo da Silva et al., 2019).
4. Effect On Microorganisms
Microbial communities in flowing aquatic ecosystems, such as zooplankton, play important roles in nutrient cycling and energy transfer in aquatic food webs (Xiong et al., 2019). As a result, environmental degradation in aquatic ecosystems can be reliably assessed by the biological response of microorganisms to environmental conditions. However, contamination has a significant impact on the geographic distribution of zooplankton biodiversity, reducing its effectiveness.
Remedial Measures
Many remedial methods have been proposed, including biological, chemical, and physical methods. However, the focus should be on methods that root out pollution so that the already affected environment can be treated quickly and realistically. Physical methods of soil treatment do not change the physicochemical properties of pollutants accumulated in the environment being treated. On the other hand, chemical methods break down the accumulated pollutants and further change their physico-chemical properties to reduce the ecological threat. More importantly, biological methods based on the biological activity of microorganisms and higher plants can reduce accumulated pollutants and even lead to their mineralization, stabilization or removal.
The implementation of the 2030 Agenda (Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development) is proposed, which will provide a framework aimed at developing a more sustainable future for humanity and the sustainable use of the natural resources on which we depend. are (Barboza et al., 2019). Recent studies have also suggested specific areas of research and innovation, such as understanding and reducing plastic use, cleaning oceans and coasts, alternative materials, and understanding the impacts on human and animal health (Barnes, 2019). In other words, workshops, conferences, seminars and the use of media can help educate people about how to manage and improve the relationship between human society and the environment in an integrated and sustainable manner.
Conclusion
This article provides an overview of environmental pollution, its causes and effects, and ways to reduce pollution. Among environmental pollution, air pollution has been widely studied and received much attention. This may be due to the increased morbidity and premature mortality caused by air pollution. Developed and developing countries share the burden of pollution, but the latter suffer the most due to weak laws, lack of awareness and poor people. Pollution disproportionately affects vulnerable groups in middle-income and low-income countries. To raise awareness about the dangers of environmental pollution and to restore the already affected environment, everyone should take part in stopping activities that promote pollution. Among other treatment methods, biological methods using microorganisms are considered environmentally friendly, cost-effective and sustainable to protect the environment and people.
Read Also:
- Environmental Pollution
- Causes Of Environmental Pollution
- Awareness Note On Mobile Tower Radiation & Its Impacts On Environment
- Extents Of Environmental Degradation
- Introduction to Environmental Degradation: Causes and Effects







Leave a Reply